상세 컨텐츠
본문
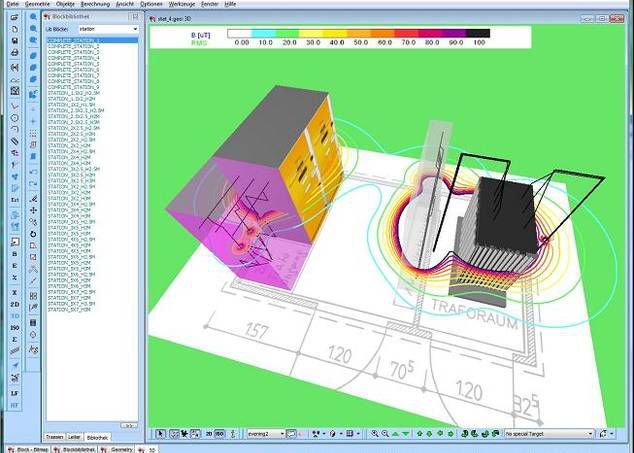
EMF and EMI are two closely related concepts in engineering, but they refer to slightly different things.
EMF, or Electromagnetic Field, is a physical field that is generated by electrically charged objects. It is the fundamental cause of all electromagnetic phenomena, including electric and magnetic fields, electric currents, and light. EMF is typically measured in units of volts per meter (V/m), and it can be either static (i.e., constant over time) or dynamic (i.e., changing over time).
EMI, or Electromagnetic Interference, is the disturbance that is caused by the emission of electromagnetic energy. This disturbance can interfere with the normal operation of electrical and electronic systems, causing them to malfunction or perform poorly. EMI can be caused by a variety of sources, including electrical power lines, radio transmitters, and electronic devices. EMI is typically measured in units of decibels (dB), and it can be either radiated (i.e., transmitted through the air) or conducted (i.e., transmitted through physical connections).
In summary, EMF is a physical field that is generated by electrically charged objects, while EMI is the disturbance that is caused by the emission of electromagnetic energy. Both EMF and EMI are important concepts in engineering, and they are typically studied in order to understand and manage the impact of electromagnetic phenomena on electrical and electronic systems.
'발전플랜트' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 송전, 배전선로 보호협조 관련 자료 (첨부) (0) | 2021.12.12 |
|---|---|
| 전기 기본이론 자료 (1) | 2021.12.12 |
| Galvanizing 용어 정리 및 관련 규격 (0) | 2020.05.29 |
| Holland Energy Park - 설계 관점에서의 시사점 공유 (3) | 2019.11.20 |
| Galvanazing Thickness 변환 (1) | 2019.10.01 |






댓글 영역